摘要
纤维素纳米晶体(Cellulose Nanocrystals, CNC)是由天然纤维素经过化学或者物理处理而获得的一种纳米材料,因其独特、优异的物理和化学性质在生物医学、电子器件等领域受到了广泛关注。近年来,CNC的绿色可持续制备得到了广泛研究。本文首先简单介绍了制备CNC的传统方法,指出了各自的优缺点,尤其是其对环境的友好程度;然后进一步重点介绍了近几年发展的绿色可持续制备CNC的新方法,主要包括有机酸水解法、固体酸水解法、亚临界水解法、离子液体处理、低共熔溶剂处理、氧化降解法以及电子束辐射法等;最后展望了CNC未来的研究方向。
作为地球上储量最丰富的天然高分子化合物,纤维素被认为是将来代替煤炭、化石燃料等不可再生资源的理想选
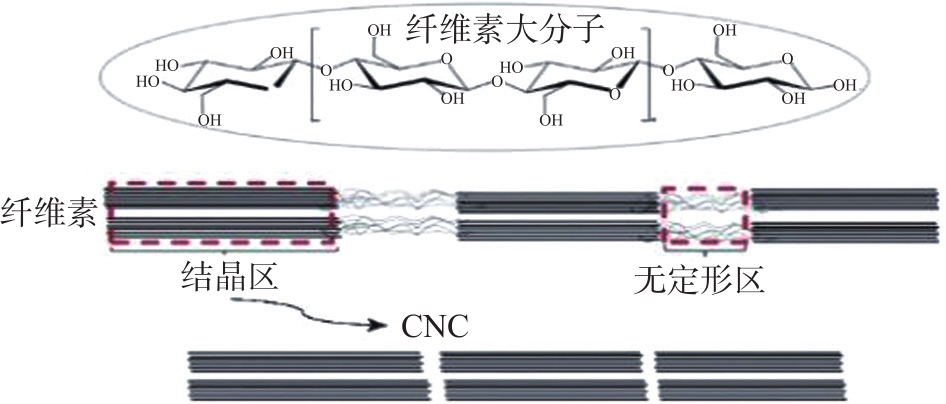
图1 酸水解纤维素制备CNC的原理
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of preparation of CNC by acid hydrolysis of cellulos
由于传统无机酸水解法不仅会对设备造成腐蚀,而且存在能耗高、废液不可回收等缺点,不符合环境友好型发展的要求。酶水解法制备CNC存在得率低、成本高、表面电荷低、分散性差等缺
继无机酸水解制备CNC之后,有机酸水解法逐渐引起了研究者的广泛关注。目前甲酸、乙酸、马来酸、草酸、对甲苯磺酸等有机酸已成功用于制备CNC。其中固体有机酸可通过重结晶回收,液体有机酸可通过减压蒸馏回收。Chen等
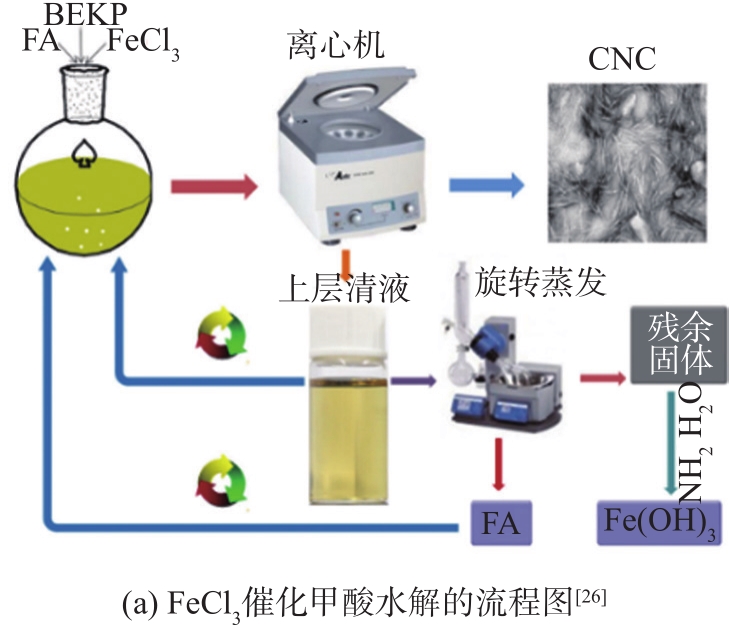
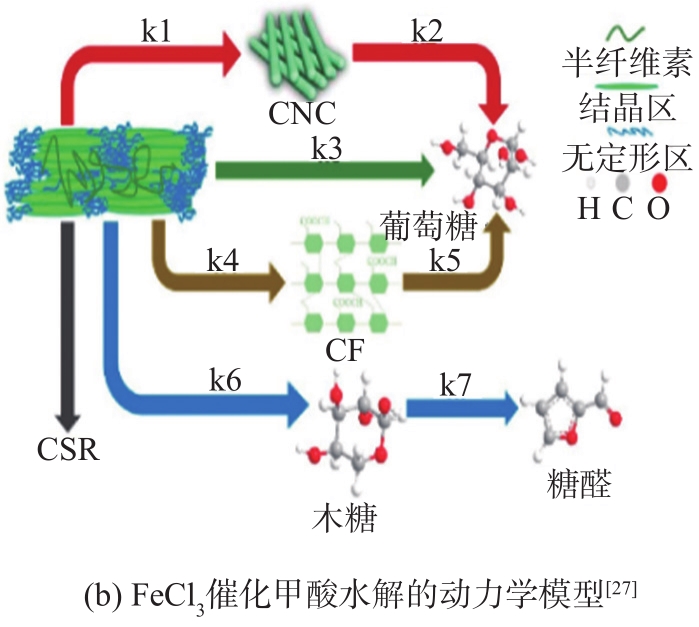
图2 FeCl3催化甲酸水解的流程图和动力学模型
Fig. 2 Flowchart and kinetic model of FeCl3 catalyzed formic acid hydrolysis
相较于无机酸水解,利用有机酸水解制备CNC的方法不仅反应条件温和、废液可回收、对设备的腐蚀性较小、对环境友好、符合绿色可持续发展的要求,而且可以通过控制酸水解反应调控CNC的形貌和理化性质,并可同步实现对CNC的功能化改性,使其可以应用于不同领域。但是,由于有机酸的酸性较弱,导致制备过程中的反应速率较慢,CNC得率较低,需要借助机械处理(如超声波)、加入催化剂等方式提高水解效率。
固体酸水解法制备CNC是近年来开发出的一种新型环保的制备工艺。Tang等
磷钨酸水解法解决了传统无机酸水解法废液量大、腐蚀严重、过度降解等问题;阳离子交换树脂的稳定性和催化活性较高,制备过程简单可控,绿色高效。固体酸水解法制备条件较温和,得率较高,可实现固体酸的回收利用,对环境友好。但是反应效率相对较低,反应时间较长,需要借助一些辅助手段(如超声波)来加快反应速率,缩短反应时间。
当物质处于亚临界状态时,分子的扩散性能增强,从而致使传质速度加快,进而对天然产物中非极性或者弱极性的物质具有较强的溶解能力及渗透性。2015年,Novo等
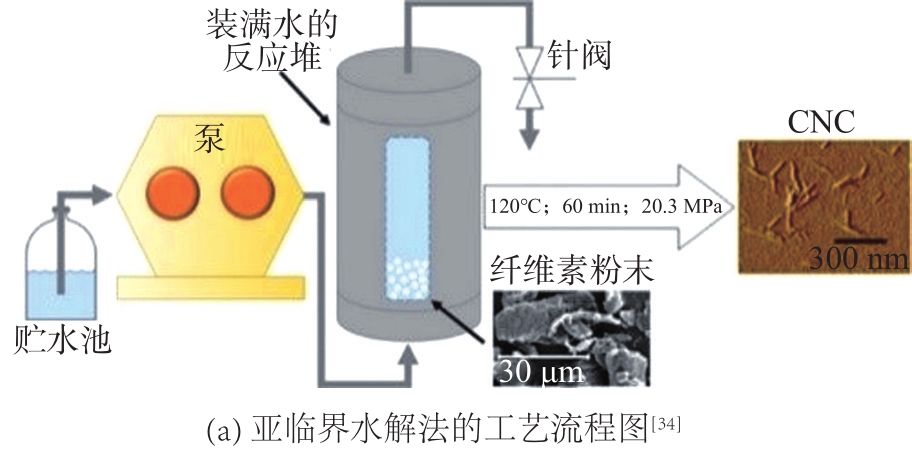
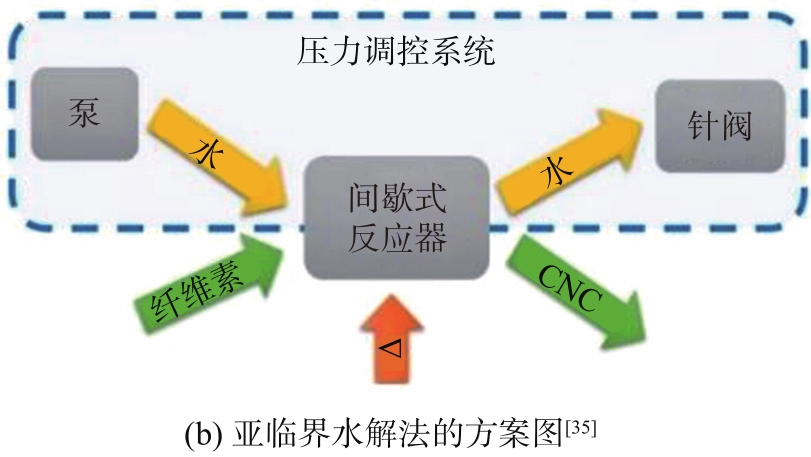
图3 亚临界水解法制备CNC的工艺流程图和方案图
Fig. 3 Process flowchart and scheme diagram of subcritical hydrolysis for CNC preparation
亚临界水解法为制备CNC提供了一种新思路,研究表明该方法的制备成本比传统硫酸法低了大约77倍,省去了透析、水洗等繁琐步骤,可节约水资源和化学药品,减少废液的产生量,提供了一种绿色环保制备CNC的方法。但此方法要求高温高压环境,对实验设备的要求较高,并且能耗较大。另外所制备的CNC表面缺少功能性基团,分散性较差。
离子液体(Ionic Liquid,IL)是在室温或者室温附近温度下呈液态的物质。IL的蒸汽压极低,对有机物和无机物均具有优异的溶解性能,可操作温度范围广,具有优异的化学和热稳定性,并可循环回收。IL作为新型绿色溶剂之一,近年来逐渐受到重视,IL可以作为预处理手段辅助制备CNC,也可以作为催化剂水解纤维素制备CNC。
Man等
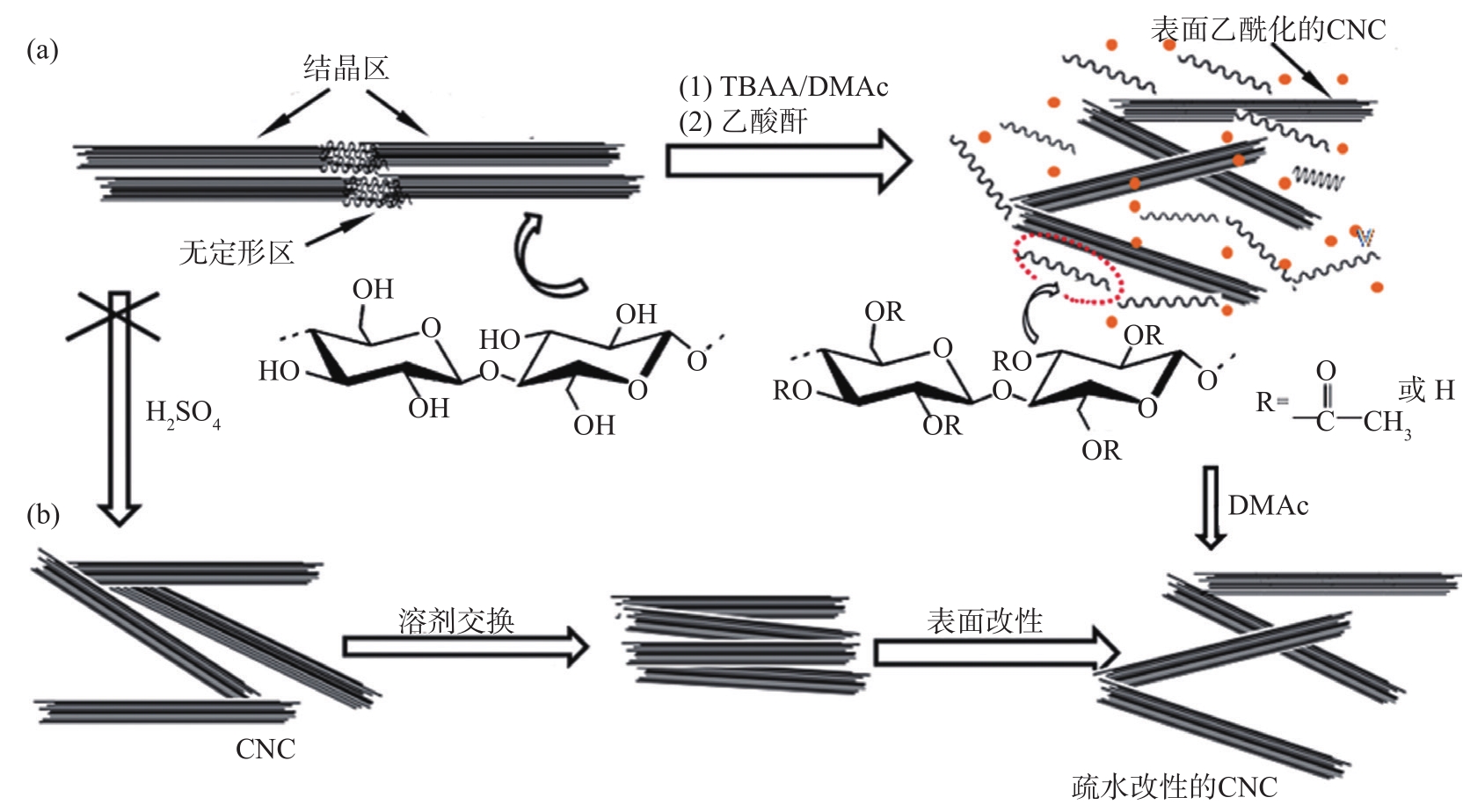
图4 以TBAA/DMAc和乙酸酐一锅法制备疏水性CNC(a)和传统制备方法(b
Fig. 4 One-pot preparation of hydrophobic CNC in TBAA/ DMAC with acetic anhydride (a) and traditional preparation method (b
IL处理可以制备功能化的CNC,并且IL可以回收利用,但是IL价格昂贵、具有毒性、回收成本较高。因此,开发出新型的高效、安全、经济的IL是未来主要研究方向之一。
低共熔溶剂(Deep Eutectic Solvents,DES)是由氢键受体(如季铵盐、两性离子)和氢键供体(如酰胺、羧酸和多元醇等化合物)组合而成的混合
Sirvio等
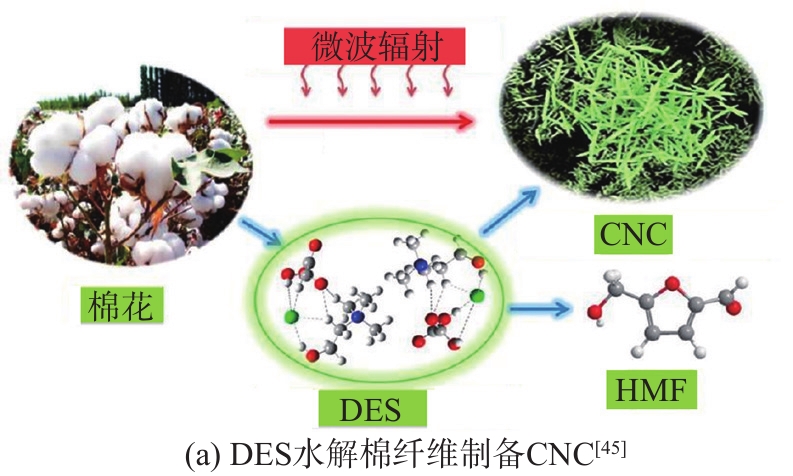
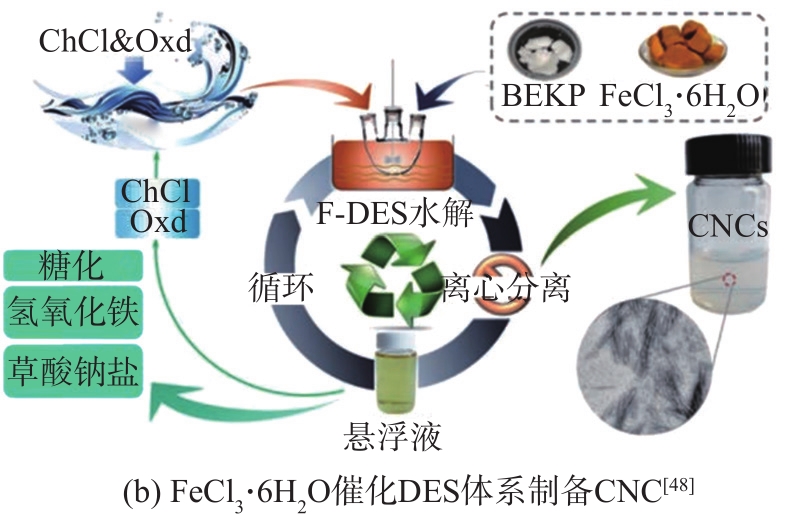
图5 DES处理制备CNC的流程图
Fig. 5 Flowchart of DES treatment for CNC preparation
上述方法中DES无法将纤维素直接降解至纳米级别,需要一定的机械辅助手段,因此研究者们继续探索以期发明一种降低反应能耗的方法。Yang等
DES处理法制备的CNC得率较高,热稳定性较高,可以通过选择不同的DES组合和控制反应条件,实现对产品性质和形貌的可控制备。另外,DES可回收、可生物降解、对环境友好,但是反应效率较低,大部分情况下需要结合后续机械处理才能得到CNC。因此,DES与纤维素的反应机理仍需进一步探索。通过开发高效催化剂,经DES处理一步法制备CNC具有较好的发展前景。
高碘酸盐可以将葡萄糖单元的C2位和C3位的羟基氧化为醛基,使C2—C3键断裂,生成2-3双醛纤维素,在许多应用中有着重要地位。Liu等
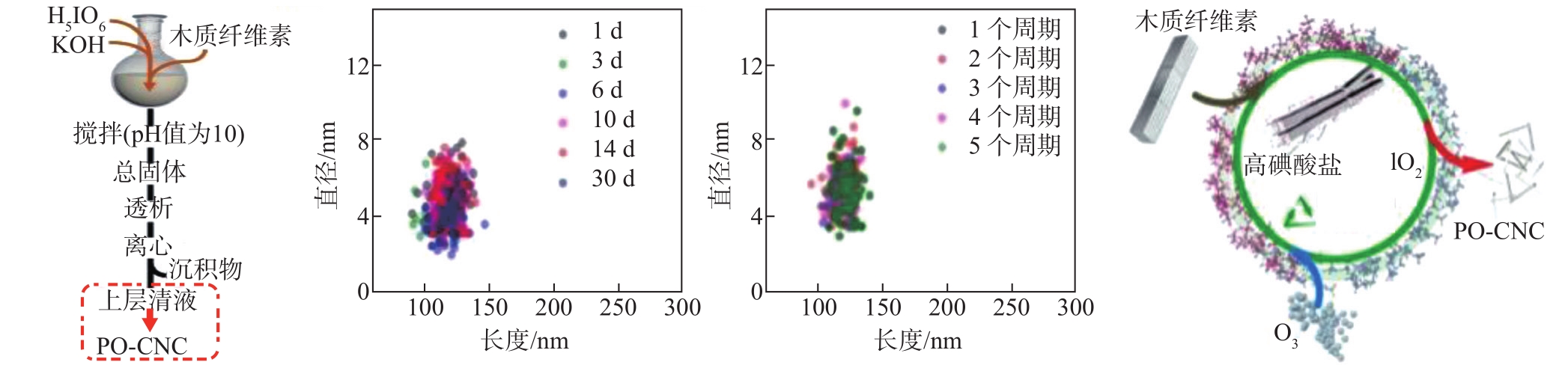
图6 高碘酸钾氧化法制备CNC的流程图、CNC的尺寸分布关系图和反应体系循环过程示意
Fig. 6 Flowchart of the alkaline periodate oxidation for CNC preparation, size distribution diagram of the obtained CNC, and cycle process of the reaction solutio
(a) 制备CNC流程图 (b) PO-CNC尺寸分布 (c) PO-CNC的循环过程
后期Liu等
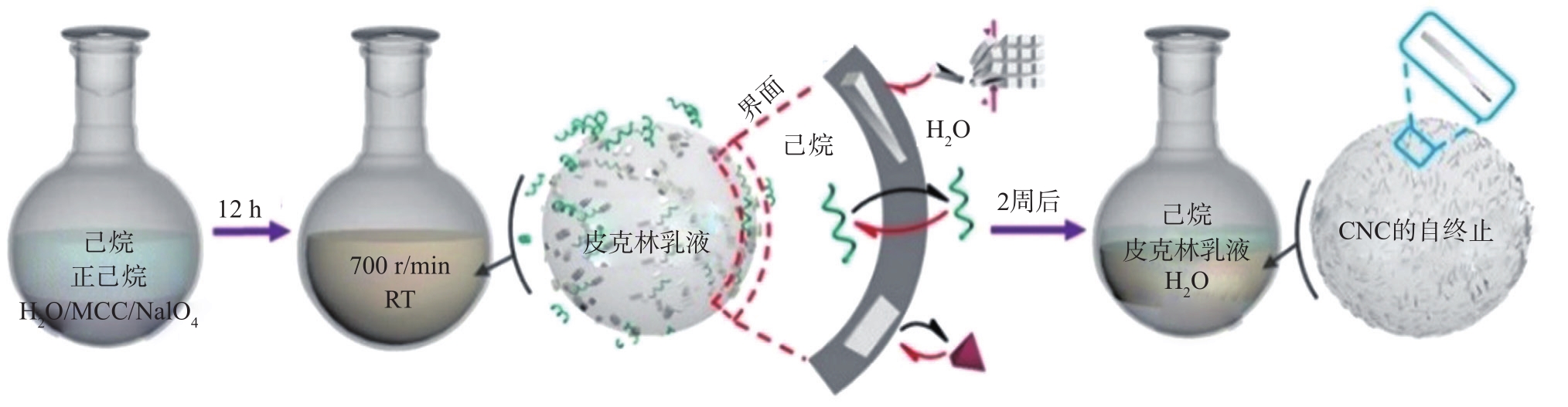
图 7 皮克林乳液中PO-CNC的合
Fig. 7 Synthesis of PO-CNC in Pickering Emulsio
Zhou等
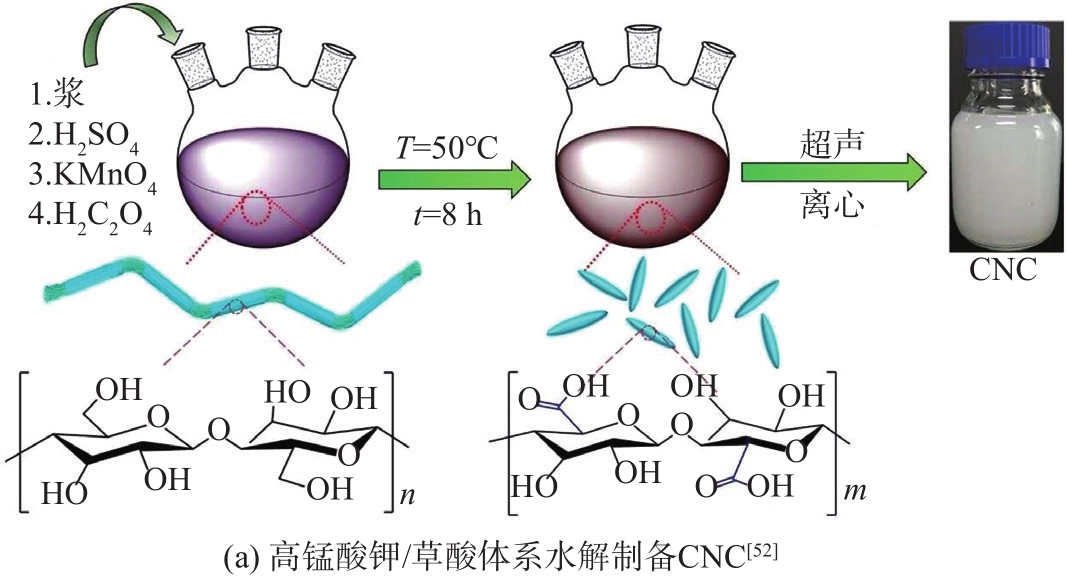
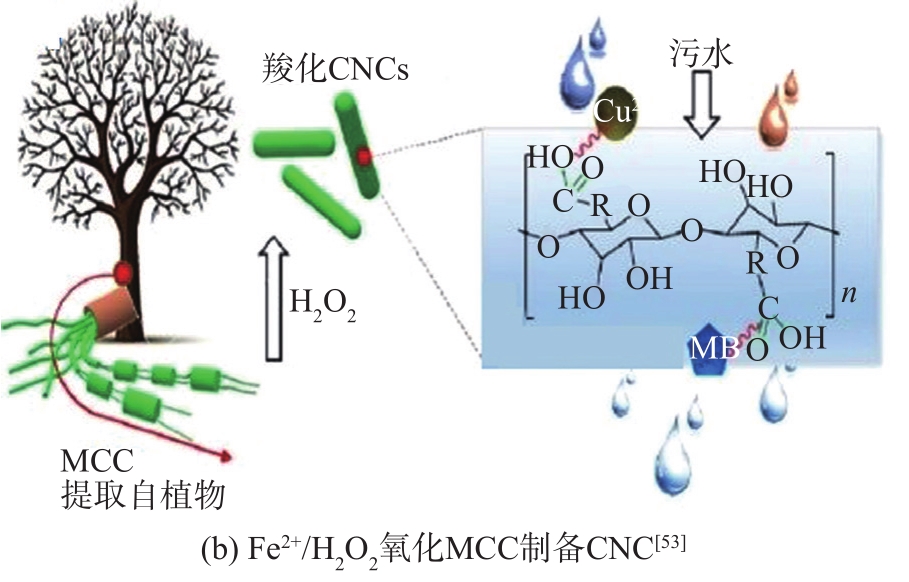
图8 氧化降解法制备CNC的流程图
Fig. 8 Flowchart of the oxidative degradation method for the preparation of CNC
Fan等
氧化降解法简单高效、能耗低,很少使用有毒试剂,无有毒副产品产生,绿色环保,CNC表面的羟基被氧化为羧基,在水中的分散稳定性较好,且具有较高的热稳定性。但制备过程中氧化剂和水用量大,反应时间相对较长。
最近研究学者发现电子束辐射(EBI)可以有效降解纤维素,使其聚合度快速降

图9 EBI、HPH结合制备CNC的工艺流程
Fig. 9 Process flowchart of EBI and HPH for the preparation of CN
电子束辐射法是一种绿色高效的预处理手段,但目前仍未有直接采用电子束辐射纤维素原料制备CNC的报道,仍需后续结合高压均质等机械处理才能得到CNC。作为一种新兴方法,电子束辐射技术用于处理纤维素原料制备CNC仍需进一步研究。
纤维素纳米晶体(CNC)作为可再生纳米材料,具有一系列优异的物化性质,可应用于污水处理、生物医药、食品、包装、光电器件等诸多领域。但制备CNC的传统方法因污染重、能耗大、成本高、腐蚀设备等缺点在一定程度上限制了CNC的大规模生产和应用。近年来,科研学者们开发了一系列绿色可持续制备CNC的方法,如有机酸水解法、氧化降解法、电子束辐射法等。以上方法在降低成本、减少能耗、回收再利用等方面取得了阶段性的突破,但是部分方法仍存在着一些不足,比如CNC得率较低,需要加入少量无机酸或金属盐作为催化剂,或者引入超声处理等辅助手段提高得率。因此,发展绿色、高效、可持续制备CNC的方法将是未来的主要研究方向之一,对CNC的规模化制备和应用具有重大意义。
参考文献
邹竹帆, 杨翔皓, 王 慧, 等. 酸水解法制备纤维素纳米晶体的研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2019, 38(3): 61-69. [百度学术]
ZHOU Z F, YANG X H, WANG H, et al. Advance in Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals by Acid Hydrolysis[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2019, 38(3): 61-69. [百度学术]
杨佳鑫, 司传领,刘 坤,等. 木质纤维生物质制备乙酰丙酸及其应用综述[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020,5(5):21-27. [百度学术]
YANG J X, SI C L, LIU K, et al. Production of levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass and application[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2020, 5(5): 21-27. [百度学术]
周丽洁, 周 欢, 李佳佳, 等. 纳米纤维素基吸油气凝胶的制备及性能[J].林业工程学报, 2019, 4(1): 67-73. [百度学术]
ZHOU L J, ZHOU H, LI J J, et al. Preparation and properties of nanocellulose-based oil-absorbing aerogels[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2019, 4(1): 67-73. [百度学术]
张 碟, 蔡 杰, 徐 威, 等. 纤维素纳米纤维水凝胶的构筑与吸附性能研究[J]. 林业工程学报, 2019, 4(2): 92-98. [百度学术]
ZHANG D, CAI J, XU W, et al. Synthesis,characterization and adsorption property of cellulose nanofiber-based hydrogels[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2019, 4(2): 92-98. [百度学术]
杜海顺,刘 超,张苗苗,等. 纳米纤维素的制备及产业化[J]. 化学进展, 2018,30(4):448-462. [百度学术]
DU H S, LIU C, ZHANG M M, et al. Preparation and Industrialization Status of Nanocellulose[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2018, 30(4): 448-462. [百度学术]
徐 蕊, 司传领, 孔凡功, 等. γ-戊内酯的制备及其在纤维素生物质转化方面的应用[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020,5(2):20-28. [百度学术]
XU R, SI C L, KONG F G, et al. Synthesis of γ-valorolactic and its application in biosmass conversion[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2020, 5(2): 20-28. [百度学术]
FILSON P B, DAWSON-ANDOH B E, SCHWEGLER-BERRY D. Enzymatic-mediated production of cellulose nanocrystals from recycled pulp[J]. Green Chemistry, 2009,11(11):1808-1814. [百度学术]
MOON R J, MARTINI A, NAIRN J, et al. Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011,40(7):3941-3994. [百度学术]
MORADBAK A, TAHIR P M, MOHAMED A Z, et al. Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from Gigantochloascortechinii ASAM pulp[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2018,76(3):1021-1027. [百度学术]
NADUPARAMBATH S, JINITHA T V, SHANIBA V, et al. Isolation and characterisation of cellulose nanocrystals from sago seed shells[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018,180:13-20. [百度学术]
CHENG M, QIN Z, CHEN Y, et al. Efficient Extraction of Cellulose Nanocrystals through Hydrochloric Acid Hydrolysis Catalyzed by Inorganic Chlorides under Hydrothermal Conditions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017,5(6):4656-4664. [百度学术]
SUCALDITO M R, CAMACHO D H. Characteristics of unique HBr-hydrolyzed cellulose nanocrystals from freshwater green algae (Cladophorarupestris) and its reinforcement in starch-based film[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017,169:315-323. [百度学术]
LU Q, LIN W, TANG L, et al. A mechanochemical approach to manufacturing bamboo cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2015,50(2):611-619. [百度学术]
周升和,谢启铮,郭云锋,等. 磷酸水热法制备纤维素纳米晶体及表面修饰研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019,47(S1):102-106. [百度学术]
ZHOU S H, XIE Q Z, GUO Y F, et al. Preparation of CNC by phosphate hydrothermal method and their surface modification[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2019, 47(S1): 102-106. [百度学术]
FILSON P B, DAWSON-ANDOH B E. Sono-chemical preparation of cellulose nanocrystals from lignocellulose derived materials[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009,100(7):2259-2264. [百度学术]
TONG X, SHEN W, CHEN X, et al. Preparation and mechanism analysis of morphology-controlled cellulose nanocrystals via compound enzymatic hydrolysis of eucalyptus pulp[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020,137(9):48407. [百度学术]
CHEN X, DENG X, SHEN W, etal. Controlled Enzymolysis Preparation of Nanocrystalline Cellulose from Pretreated Cottod Fi⁃bers[J]. BioResources, 2012,7(3):4237-4248. [百度学术]
刘 慰,司传领,杜海顺,等. 纳米纤维素基水凝胶的制备及其在生物医学领域的应用进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2019,4(5):11-19. [百度学术]
LIU W, SI C L, DU H S, et al. Advance in preparation of nanocellulose-based hydrogels and their biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2019, 4(5): 11-19. [百度学术]
CHEN L, ZHU J Y, BAEZ C, et al. Highly thermal-stable and functional cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils produced using fully recyclable organic acids[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016,18(13):3835-3843. [百度学术]
BIAN H, CHEN L, DAI H, et al. Integrated production of lignin containing cellulose nanocrystals (LCNC) and nanofibrils (LCNF) using an easily recyclable di-carboxylic acid[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017,167:167-176. [百度学术]
XU W, GRENMAN H, LIU J, et al. Mild Oxalic-Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis as a Novel Approach to Prepare Cellulose Nanocrystals[J]. Chemnanomat, 2017,3(2):109-119. [百度学术]
JI H, XIANG Z, QI H, et al. Strategy towards one-step preparation of carboxylic cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils with high yield, carboxylation and highly stable dispersibility using innocuous citric acid[J]. Green Chemistry, 2019,21(8):1956-1964. [百度学术]
LIU W, DU H, LIU H, et al. Highly Efficient and Sustainable Preparation of Carboxylic and Thermostable Cellulose Nanocrystals via FeCl3-Catalyzed Innocuous Citric Acid Hydrolysis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020,8(44):16691-16700. [百度学术]
LI B, XU W, KRONLUNG D, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals prepared via formic acid hydrolysis followed by TEMPO-mediated oxidation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015,133:605-612. [百度学术]
LIU C, LI B, DU H, et al. Properties of nanocellulose isolated from corncob residue using sulfuric acid, formic acid, oxidative and mechanical methods[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016,151:716-724. [百度学术]
DU H, LIU C, MU X, et al. Preparation and characterization of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals via a sustainable approach of FeCl3-catalyzed formic acid hydrolysis[J]. Cellulose, 2016,23(4):2389-2407. [百度学术]
LYU L, DU H S, CHE X P, et al. Tailored and Integrated Production of Functional Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibrils via Sustainable Formic Acid Hydrolysis: Kinetic Study and Characterization[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engine⁃ering, 2019, 7(10): 9449-9463. [百度学术]
TANG L, HUANG B, OU W, et al. Manufacture of cellulose nanocrystals by cation exchange resin-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011,102(23):10973-10977. [百度学术]
LIU Y, WANG H, YU G, et al. A novel approach for the preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose by using phosphotung⁃sticacid[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2014,110:415-422. [百度学术]
卢燕凤,吴耿烽,曾常伟,等. 原位合成炭基磷钨酸及其催化性能初探[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2015(4):48-52. [百度学术]
LU Y F, WU G F, ZENG C W, et al. In-situ Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of Carbon-based Phosphotungstic Acid[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2015(4): 48-52. [百度学术]
尚倩倩,刘承果,胡立红,等. 超声辅助磷钨酸催化制备纳米纤维素及其表征[J]. 化学工程与技术, 2017,7(6):241-248. [百度学术]
SHANG Q Q, LIU C G, HU L H, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Cellulose by Using Sonication Combination with Phosphotungstic Acid[J]. Hans Journal of Chemical Engineering and Technology, 2017, 7(6): 241-248. [百度学术]
游惠娟, 曾常伟, 卢麒麟, 等. 炭基磷钨酸催化制备纳米纤维素的研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2014(2):100-103. [百度学术]
YOU H J, ZENG C W, LU Q L, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Cellulose Catalyzed by Carbon-Based Phosphotungstic Acid [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2014(2): 100-103. [百度学术]
TORLOPLV M A, UDORATINA E V, MARTAKOV I S, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals prepared in H3PW12O40-acetic acid system[J]. Cellulose, 2017,24(5):2153-2162. [百度学术]
NOVO L P, BRAS J, GARCIA A, et al. Subcritical Water: A Method for Green Production of Cellulose Nanocrystals[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015,3(11):2839-2846. [百度学术]
NOVO L P, BRAS J, GARCIA A, et al. A study of the production of cellulose nanocrystals through subcritical water hydrolysis[J]. Industrial Cropsand Products, 2016,93:88-95. [百度学术]
MAN Z, MUHAMMAD N, SARWONO A, et al. Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals Using an Ionic Liquid[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2011,19(3):726-731. [百度学术]
LAZKO J, SENECHAL T, LANDERCY N, et al. Well defined thermostable cellulose nanocrystals via two-step ionic liquid swelling-hydrolysis extraction[J]. Cellulose, 2014,21(6):4195-4207. [百度学术]
MAO J, HECK B, REITER G, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals' production in near theoretical yields by 1-butyl-3-methylimi⁃dazolium hydrogen sulfate ( [Bmim]HSO4)-mediated hydrolysis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015,117:443-451. [百度学术]
ABUSHAMMALA H, KROSSING I, LABORIE M. Ionic liquid-mediated technology to produce cellulose nanocrystals directly from wood[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015,134:609-616. [百度学术]
MIAO J, YU Y, JIANG Z, et al. One-pot preparation of hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals in an ionic liquid[J]. Cellulose, 2016,23(2):1209-1219. [百度学术]
张筱仪, 刘 慰, 刘华玉, 等. 基于低共熔溶剂的木质纤维生物质预处理及其高值化利用的研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2020, 39(8): 85-93. [百度学术]
ZHANG X Y, LIU W, LIU H Y, et al. Research Advances of Pretreatment and High Value Utilization of Lignocellulosic Biomass Based on Deep Eutectic Solvents[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2020, 39(8): 85-93. [百度学术]
廖可瑜, 吴美燕, 刘 超, 等. 低共熔溶剂在纳米纤维素制备中的应用和研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2020, 39(2): 65-72. [百度学术]
LIAO K Y, WU M Y, LIU C, et al. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvent in Preparation of Nanocellulose and Its Research Progress[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2020, 39(2): 65-72. [百度学术]
SIRVIO J A, VISANKO M, LIIMATAINEN H. Deep eutectic solvent system based on choline chloride-urea as a pre-treatment for nanofibrillation of wood cellulose[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(6): 3401-3406. [百度学术]
SIRVIO J A, VISANKO M, LIIMATAINEN H. Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvents As HydrolyticMedia for Cellulose Nanocrystal Production[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2016,17(9):3025-3032. [百度学术]
LIU Y, GUO B, XIA Q, et al. Efficient Cleavage of Strong Hydrogen Bonds in Cotton by Deep Eutectic Solvents and Facile Fabrication of Cellulose Nanocrystals in High Yields[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017,5(9):7623-7631. [百度学术]
SIRVIO J A. Fabrication of regenerated cellulose nanoparticles by mechanical disintegration of cellulose after dissolution and regeneration from a deep eutectic solvent[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(2):755-763. [百度学术]
MA Y, XIA Q, LIU Y, et al. Production of Nanocellulose Using Hydrated Deep Eutectic Solvent Combined with Ultrasonic Treatment[J]. ACS Omega, 2019,4(5):8539-8547. [百度学术]
YANG X H, XIE H X, DU H S, et al. Facile Extraction of Thermally Stable and Dispersible Cellulose Nanocrystals with High Yield via a Green and Recyclable FeCl3-Catalyzed Deep Eutectic Solvent System[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019,7(7):7200-7208. [百度学术]
LI P, SIRVIO J A, ASANTE B, et al. Recyclable deep eutectic solvent for the production of cationic nanocelluloses[J]. Carbohyd⁃rate Polymers, 2018,199:219-227. [百度学术]
LIU P W, PANG B, DECHERT S, et al. Structure Selectivity of Alkaline Periodate Oxidation on Lignocellulose for Facile Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals[J]. Angewandte Chemie-international Edition, 2020, 59(8):3218-3225. [百度学术]
LIU P W, PANG B, TIAN L, et al. Efficient, Self-Terminating Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals through Periodate Oxidation in Pickering Emulsions[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018,11(20):3581-3585. [百度学术]
ZHOU L J, LI N, SHU J, et al. One-Pot Preparation of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals and Their Liquid Crystalline Behaviors[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018,6(9):12403-12410. [百度学术]
FAN X, YU H, WANG D, et al. Facile and Green Synthesis of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanocrystals as Efficient Adsorbents in Wastewater Treatments[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Enginee⁃ring, 2019,7(21):18067-18075. [百度学术]
崔国士,束兴娟,张蕊蕊,等. 木浆纤维素电子束辐射降解效应研究[J]. 河南科学, 2019,37(2):179-182. [百度学术]
CUI G S, SHU X J, ZHANG R R, et al. Radiation Degradation Effect of Electron Beam on Wood Pulp Cellulose[J]. Henan Science, 2019, 37(2): 179-182. [百度学术]
LEE M, HEO M H, LEE H, et al. Facile and eco-friendly extraction of cellulose nanocrystals via electron beam irradiation followed by high-pressure homogenization[J]. Green Chemistry, 2018,20(11):2596-2610. [百度学术]