摘要
本研究以酶解木质素(EHL)为原料,利用Mannich反应对其进行胺化改性,制备胺化酶解木质素(NEHL),进一步提高其对刚果红(CR)染料的识别和选择性吸附,并优选出最佳制备工艺。结果表明,利用Mannich反应可在EHL表面成功接枝胺基;改性后的NEHL微观结构发生明显的变化,从表面光滑变为表面粗糙,其表面具有由不规则颗粒组成的结构,比表面积增大。吸附实验结果表明,NEHL添加量为0.05 g时,对CR吸附量可达2 444.82 mg/g;对NEHL的吸附动力学和等温吸附模型进行分析,得出NEHL对CR进行单层化学吸附。NEHL的制备工艺简单,去除染料性能优越,是一种潜在的去除废水中CR染料的吸附剂。
合成染料在许多工业如染整、纺织、皮革鞣制、食品、塑料、造纸和制药等均有普遍应
在众多的物理和化学废水处理技术中,吸附法具有成本效益高、应用灵活及设计过程简单等优
刚果红(CR)是一种常见的合成染料,CR分子在水溶液中带负电荷,带正电荷的吸附剂可通过静电作用吸附CR染
酶解木质素(enzymatic hydrolysis lignin,EHL)是从微生物酶解玉米秸秆制备丁醇等能源的残渣中分离得到的新型木质素,与传统的碱木质素和硫酸盐木质素相比,EHL具有多种活性基团和较好的反应活
乙二胺、甲醛、NaOH均购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;盐酸购于上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司;刚果红(CR)购于上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;上述商品均为分析纯;酶解木质素(EHL)购于山东龙力生物科技股份有限公司。
将EHL在60 ℃的烘箱中干燥至质量恒定,取其中2 g EHL加入到三颈烧瓶中,加入20 mL 0.5 mol/L的NaOH溶液,超声处理30 min,EHL完全溶解于NaOH溶液;向三颈烧瓶中加入一定量的乙二胺,在30 min内缓慢滴加1.5 mL质量分数38%的甲醛水溶液,在80 ℃油浴锅中反应4 h。产物用去离子水稀释,然后用1 mol/L盐酸酸析至混合液的pH值为2~3后沉淀10 h。将沉淀置于离心机中8 000 r/min离心5 min,将沉淀用无水乙醇洗涤数次,再用去离子水洗涤至中性。将产物置于50 ℃真空干燥箱干燥后,得到所需的胺化木质素,命名为NEHL。根据甲醛和乙二胺的不同体积比制备NEHL,分别命名为NEHL-1(甲醛∶乙二胺=1∶1.4)、NEHL-2(甲醛∶乙二胺=1∶2.0)、NEHL-3(甲醛∶乙二胺=1∶2.6),比较NEHL对CR吸附性能,探究最佳制备工艺。
在一定质量浓度CR染料溶液中加入一定量的NEHL吸附剂,吸附平衡后进行过滤,用紫外分光光度计测定滤液的吸光度,根据CR标准曲线计算CR的浓度。根据
| (1) |
| (2) |
式中,C0和Ce分别为初始和吸附平衡时的CR溶液质量浓度,mg/L;V为CR溶液的体积,L;M为吸附剂的质量,g。
采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,SU8010,日本Hitachi公司)观察样品的微观形貌;使用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FT-IR,Nicolet380,美国热电公司)对样品的表面官能团进行表征;采用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,K-Alpha,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)对样品的表面化学环境进行精细分析;利用紫外分光光度计(UV,UV-6300,上海美普达仪器有限公司)检测吸附性能;采用全自动气体吸附仪(BET,ASAP 2020 Plus 2.00,美国micromeritics公司)对样品的比表面积和孔径进行检测;采用接触角测试仪(DSA30,德国Kruss公司)对样品的表面亲疏水性进行检测。
本研究以乙二胺为Mannich反应的胺化剂。木质素分子的酚羟基及其邻位和对位,以及侧链上羰基的α位上的氢原子具有活泼性,可以与醛和脂肪胺类化合物发生Mannich反
为验证EHL胺化改性成功,分别对胺化前后EHL的化学结构进行分析。
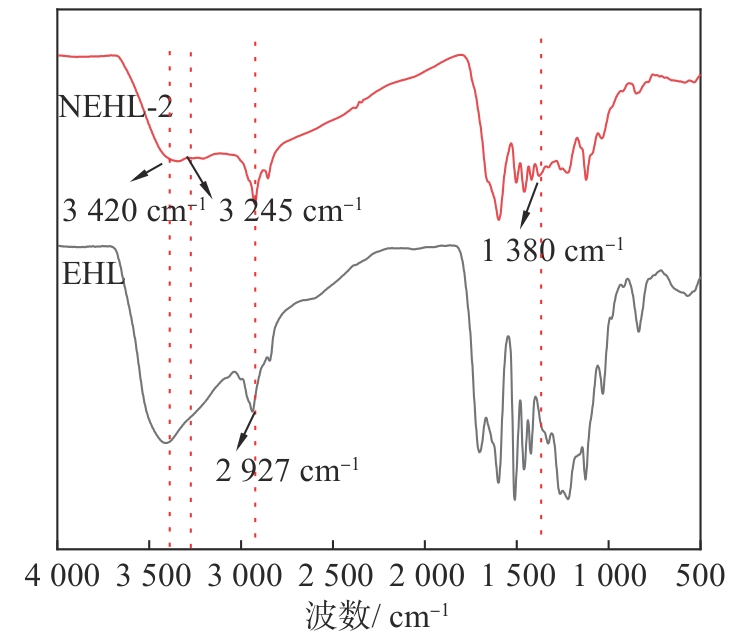
图1 EHL和NEHL-2的FT-IR谱图
Fig. 1 FT-IR spectra of EHL and NEHL-2
进一步利用XPS对比EHL胺化前后表面化学元素价态的变化情况,结果如
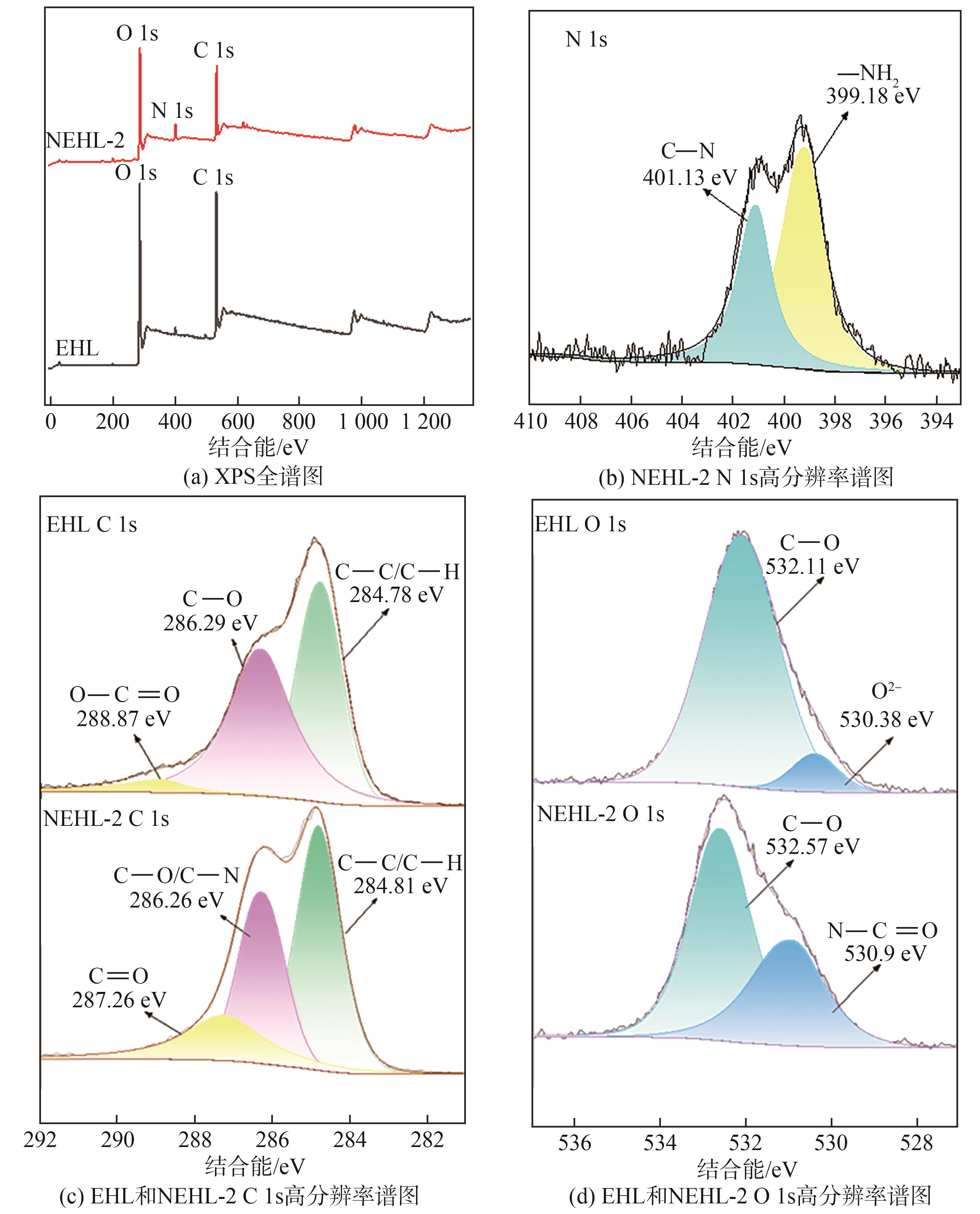
图2 EHL和NEHL-2的XPS谱图
Fig. 2 XPS spectra of EHL and NEHL-2
| 样品名称 | C | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| EHL | 74.2 | 2.18 | 23.6 |
| NEHL-2 | 71.8 | 7.92 | 20.3 |
利用SEM进一步探究EHL胺化改性前后的形貌特征,结果如

图3 EHL和NEHL-2的SEM图
Fig. 3 SEM images of EHL and NEHL-2
利用N2吸附-脱附法对样品进行测试,结果如
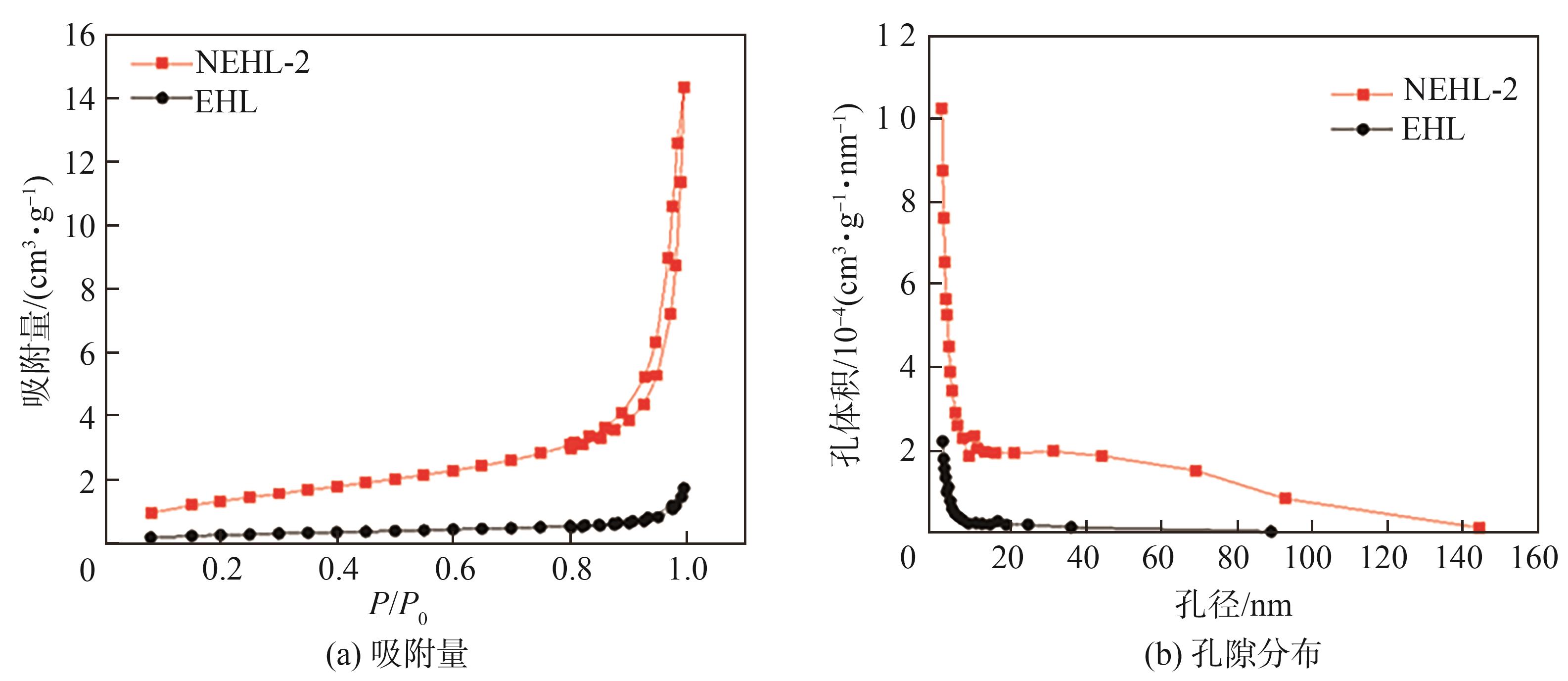
图4 EHL和NEHL-2的N2吸附-脱附测试
Fig. 4 N2 adsorption and desorption tests for EHL and NEHL-2
| 样品名称 | 比表面积/(m²· | 孔体积/(cm³· | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| EHL | 1.009 5 | 0.002 650 | 12.345 8 |
| NEHL-2 | 4.973 0 | 0.022 203 | 17.858 5 |
综上所述,本研究通过Mannich胺化反应,可在EHL中有效引入胺基官能团和其他亲水官能团(

图5 EHL和NEHL-2的水接触角
Fig. 5 Water contact angle of EHL and NEHL-2

图6 NEHL种类及添加量对吸附吸附性能的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of NEHL species and dosage on adsorption property
NEHL-2对CR的吸附效果最好,CR去除率为94.8%,是EHL的2.8倍,表明其胺化改性效果最好,因此后续表征以NEHL-2为吸附剂。
达到吸附平衡的时间是评价吸附剂优劣的因素之一。本节设置了0、15、30、45、60、75 min 6组对照实验(NEHL-2添加量0.05 g,其余吸附性能测试条件与2.2.1相同),对吸附后的CR溶液进行吸光度测量,计算每组样品CR的剩余浓度,得到CR吸附量随时间的变化关系(
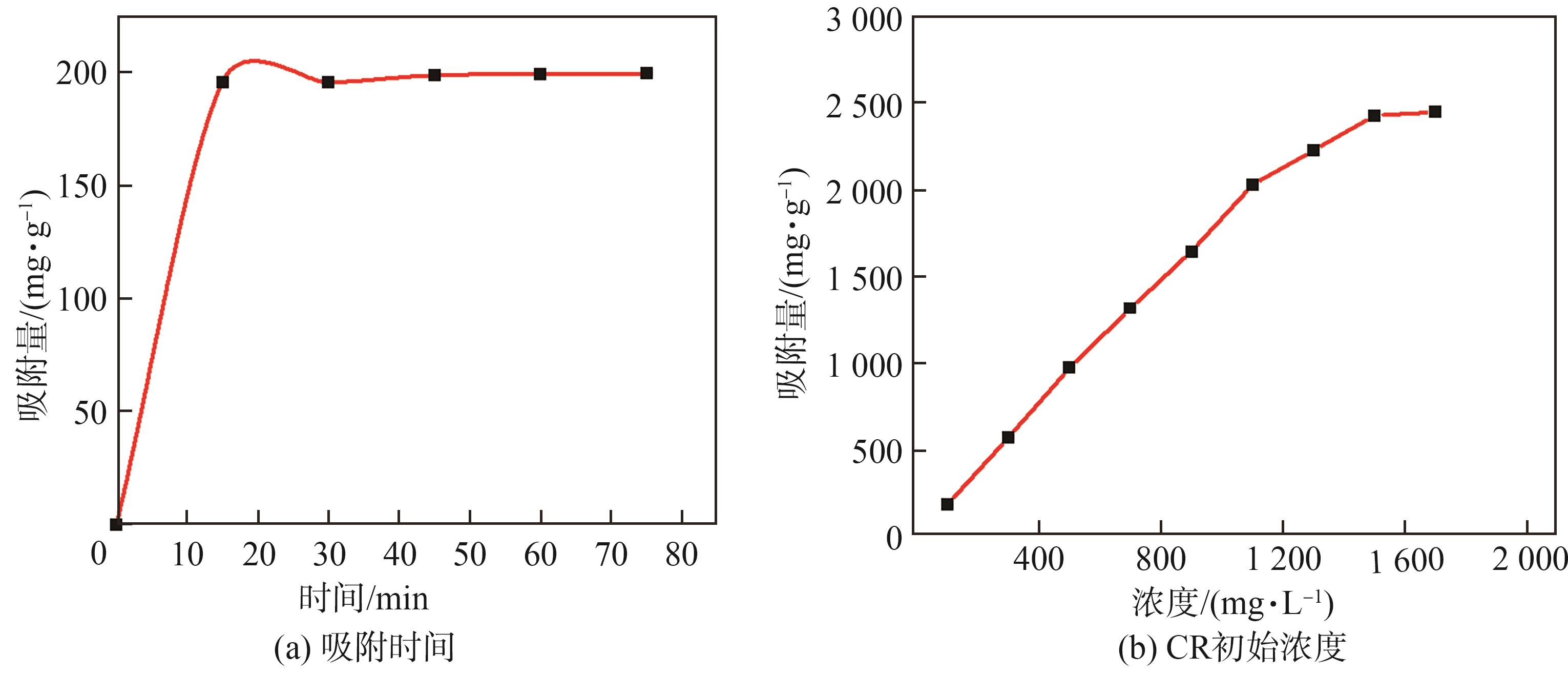
图7 吸附时间及CR初始浓度对吸附性能的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of adsorption time and CR initial concentration on adsorption property
| 吸附剂种类 | 吸附量/(mg· | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒活性炭 | 9.1 |
[ |
| 磁性埃洛石纳米管 | 41.5 |
[ |
| 分层多孔ZnO | 334.0 |
[ |
| 羧甲基纤维素活性炭 | 1 799.5 |
[ |
| 多孔壳聚糖/羧甲基纤维素-PEG水凝胶 | 1 053.9 |
[ |
| 多孔金属-有机骨架-丙烯酰胺-壳聚糖复合气凝胶 | 2 086.4 |
[ |
| 多孔Fe(OH)3 @纤维素杂化纤维 | 689.7 |
[ |
| NEHL-2 | 2 444.82 | 本研究 |
为了更好地探究吸附剂吸附CR的吸附机理,本研究采用2种吸附动力学模型对实验数据进行拟合:准一级和准二级动力学模型。准一级动力学模型(
| (3) |
| (4) |
式中,t为吸附时间,min;qt为吸附t时刻的吸附量,mg/g;k1为准一级动力学模型的吸附速率常数,即单位时间内CR分子从溶液中吸附到表面的速率,mi
NEHL-2吸附CR的准一级、准二级动力学模型拟合结果如
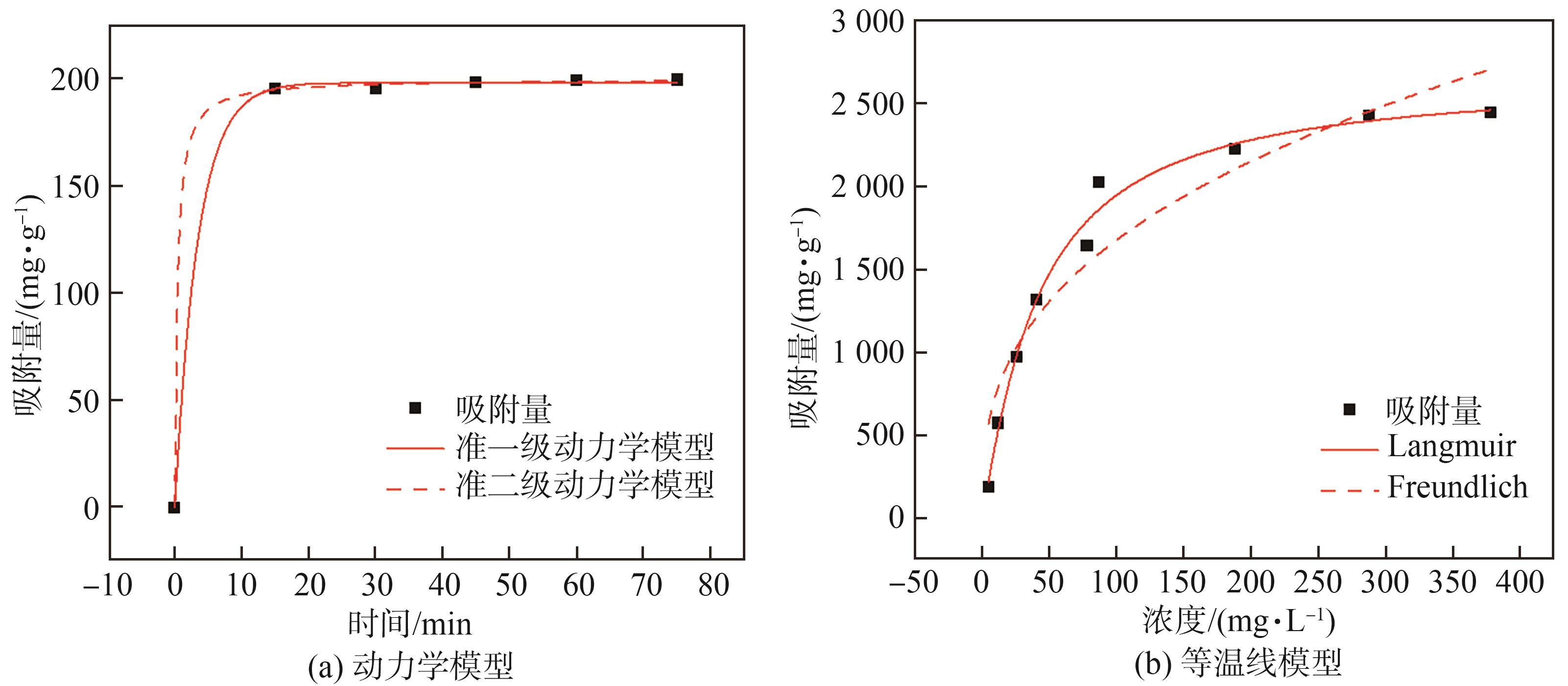
图8 NEHL-2吸附CR的动力学、等温线模型
Fig. 8 Kinetic and isotherm models of CR adsorption by NEHL-2
| 动力学模型 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| 准一级动力学模型 |
k1 /mi | 0.287 76 |
|
qe/(mg· | 198.081 01 | |
|
| 0.999 6 | |
| 准一级动力学模型 |
k2 /mi | 0.012 86 |
|
qe/(mg· | 199.873 55 | |
|
| 0.999 8 |
为了进一步探究吸附剂吸附CR的吸附机理,本研究采用Langmuir和Freundlich 2种等温吸附模型对吸附数据进行拟合。Langmuir模型(
| (5) |
| (6) |
式中,qm为最大吸附量,mg/g;ce为达到平衡吸附后的CR浓度,mg/L;kL和kF分别为Langmuir吸附常数和Freundlich吸附常数。
| 等温吸附模型 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir |
kL/(L·m | 0.013 89 |
|
qm/(mg· | 2 654.473 03 | |
|
| 0.986 8 | |
| Freundlich |
kF/(mg· | 318.400 72 |
| n | -0.360 63 | |
|
| 0.897 12 |
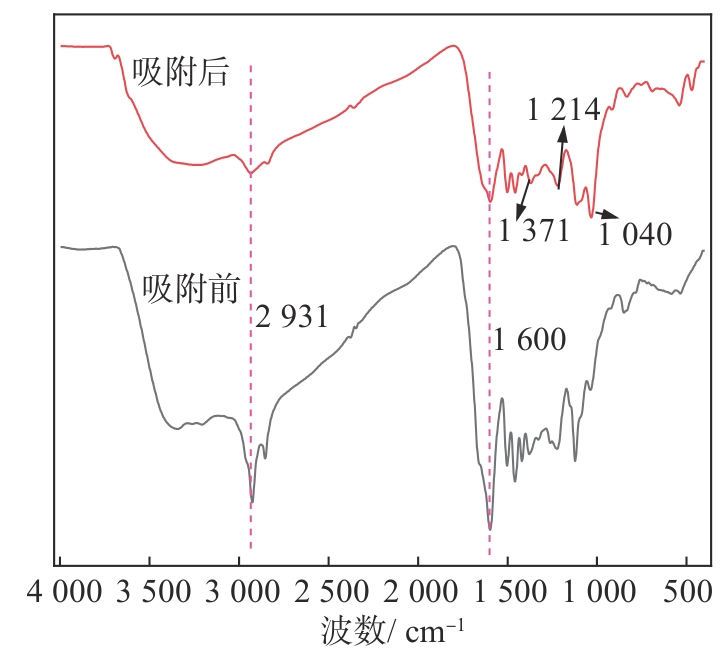
图9 NEHL-2吸附CR前后的FT-IR谱图
Fig. 9 FT-IR spectra before and after NEHL-2 adsorption of CR
因此,CR的吸附机理可归结于:①NEHL中质子化胺基与CR中的阴离子磺酸盐之间的静电吸引;②NEHL和CR的质子化胺基与NEHL和CR的芳香环之间的阳离子NH-π相互作用;③NEHL的胺或羟基与CR中的胺、偶氮或磺酸基团之间的氢键相互作用;④NEHL和CR的芳环之间的π-π相互作用(
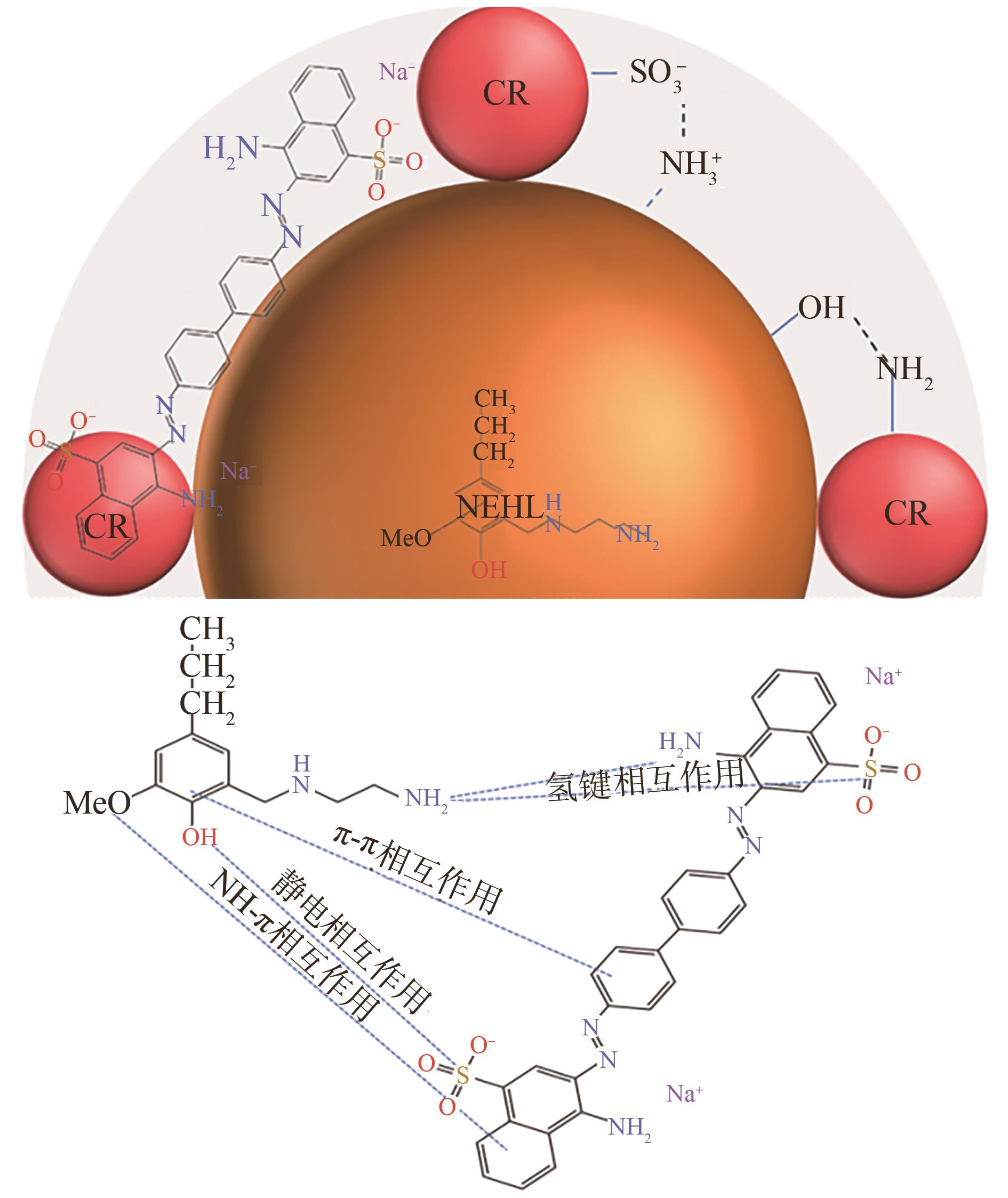
图10 NEHL吸附CR的机理
Fig 10 Mechanism of adsorption of CR by NEHL
本研究主要以酶解木质素(EHL)为原料,通过Mannich反应对其进行胺化改性,制备胺化酶解木质素(NEHL),用于刚果红(CR)染料的高效吸附。
3.1 通过红外光谱、X射线能谱和表面形貌分析,表明胺基被成功接枝到EHL上,同时NEHL整体由不规则颗粒连结而成,具有较大的比表面积,使得NEHL具有更好的吸附性能。
3.2 通过吸附实验,得出NEHL能在水中快速吸附CR,并表现出较高的CR去除率,CR吸附遵循准二级动力学、Langmuir等温吸附模型,CR饱和吸附量为2 444.82 mg/g。CR的吸附机理主要涉及静电、氢键、NH-π和π-π相互作用。
参考文献
YAGUB M T, SEN T K, AFROZE S,et al. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 209: 172-184. [百度学术]
WANG C, FENG X, SHANG S, et al. Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution with lignin-modified metal-organic frameworks: Selective adsorption and high adsorption capacity[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129781. [百度学术]
宋长永,高超,刘忠明,等.木质素的氨化改性及其对孔雀石绿的吸附性能研究[J].中国造纸,2023,42(12):61-69. [百度学术]
SONG C Y, GAO C, LIU Z M, et al. Study on Ammonia Modification of Lignin and Its Adsorption Properties for Malachite Green [J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2019, 42(12):61-69. [百度学术]
TIAN Y, ZHANG H, PAN S, et al. Amine-functionalized magnetic microspheres from lignosulfonate for industrial wastewater purification[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 224: 133-142. [百度学术]
ABDELHAMID H N, ZOU X. Template-free and room temperature synthesis of hierarchical porous zeolitic imidazolate framework nanoparticles and their dye and CO2 sorption[J]. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(5): 1074-1084. [百度学术]
MIRZAEI N, MAHVI A H, HOSSINI H. Equilibrium and kinetics studies of direct blue 71 adsorption from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite[J]. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2017, 36(1/2): 80-94. [百度学术]
SUN Y, WANG T, HAN C, et al. One-step preparation of lignin-based magnetic biochar as bifunctional material for the efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Congo red: Performance and practical application[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128373. [百度学术]
OLIVEIRA E H C D, MARQUES F D M D S, DA S M P, et al. Removal of toxic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto highly recyclable xGn
WALLING B, BHARALI P, RAMACHANDRAN D, et al. In-situ biofabrication of bacterial nanocellulose(BNC)/graphene oxide (GO) nano-biocomposite and study of its cationic dyes adsorption properties[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126309. [百度学术]
OBAYOMI K S, LAU S Y, DANQUAH M K, et al. Green synthesis of graphene-oxide based nanocomposites for efficient removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater[J]. Desalination, DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2023.116749. [百度学术]
LI L, LIU X, DUAN T, et al. Construction of Cu-N coordination into natural biopolymer lignin backbone for highly efficient and selective removal of cationic dyes[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.128841. [百度学术]
ALATALO S M, MÄKILÄ E, REPO E, et al. Meso- and microporous soft templated hydrothermal carbons for dye removal from water[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(4): 1137-1146. [百度学术]
KOOHI P, RAHBAR-KELISHAMI A, SHAYESTEH H. Efficient removal of Congo red dye using Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposite: Synthesis and characterization[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, DOI: 10.1016/j.eti.2021.101559. [百度学术]
张召慧,吴朝军,于冬梅,等. 木质素基吸附剂的研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2021,40(1):106-117. [百度学术]
ZHANG Z H, WU C J, YU D M, et al. Research Progress of Lignin-Based Adsor-bents [J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2021, 40(1): 106-117. [百度学术]
刘丹丹,邵礼书,刘娜,等. 氮氧共修饰木质素基多孔树脂的制备及其对染料的高效吸附[J].中国造纸,2023,42(5): 107-118. [百度学术]
LIU D D, SHAO L S, LIU N, et al. Preparation of Nitrogen-oxygen Co-modified Lignin-based Polyporous Resin and Its Efficient Adsorption of Dyes [J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2023, 42(5): 107-118. [百度学术]
PAANANEN H, ALVILA L, PAKKANEN T T. Hydroxymethylation of softwood kraft lignin and phenol with paraformaldehyde[J]. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, DOI: 10.1016/j.scp.2021.100376. [百度学术]
YANG W, DING H, QI G, et al. Enhancing the Radical Scavenging Activity and UV Resistance of Lignin Nanoparticles via Surface Mannich Amination toward a Bio-based Antioxidant[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2021, 22(6): 2693-2701. [百度学术]
TRAN N T, KO Y, KIM S, et al. Microwave-assisted phenolation of acid-insoluble Klason lignin and its application in adhesion[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(5): 2051-2061. [百度学术]
SHAN X, ZHAO Y, BO S, et al. Magnetic aminated lignin/CeO2/Fe3O4 composites with tailored interfacial chemistry and affinity for selective phosphate removal[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148984. [百度学术]
WANG X H, ZHANG Y K, HAO C, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of aminated lignin by a Mannichreaction and its decolorizing properties for anionic azo-dyes[J]. RSC Advances, 2014,4(53):28156-28164. [百度学术]
HEO J W, AN L, CHEN J, et al. Preparation of amine functionalized lignins for the selective adsorption of Methylene blue and Congo red[J]. Chemosphere. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133815. [百度学术]
李燕. 秸秆酶解木质素液化改性及聚氨酯发泡材料制备研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2012. [百度学术]
LI Y. Liquefaction modification of lignin by enzymatic hydrolysis of straw and preparation of polyurethane foam materials [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry,2012. [百度学术]
WANG M, SJÖHOLM E, LI J. Fast and reliable quantification of lignin reactivity via reaction with dimethylamine and formaldehyde (Mannich reaction)[J]. 2017, 71(1): 27-34. [百度学术]
KAWASAKI T, ZEN H, SAKAI T, et al. Degradation of Lignin by Infrared Free Electron Laser[J]. Polymers, DOI: 10.3390/polym14122401. [百度学术]
GUO Y, XU L, SHEN F, et al. Insights into lignocellulosic waste fractionation for lignin nanospheres fabrication using acidic/alkaline deep eutectic solvents[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131798. [百度学术]
SZABÓ L, MILOTSKYI R, UEDA H, et al. Controlled acetylation of kraft lignin for tailoring polyacrylonitrile-kraft lignin interactions towards the production of quality carbon nanofibers[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 1016/j.cej.2020.126640. [百度学术]
ZHU J, LUO Y, WANG J, et al. Highly efficient uranium extraction by aminated lignin-based thermo-responsive hydrogels[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120744. [百度学术]
ZHANG B, ZHANG H, WANG Y, et al. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of amine/quaternary ammonium lignin on tungsten[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.226. [百度学术]
PANG Y, CHEN Z, ZHAO R, et al. Facile synthesis of easily separated and reusable silver nanoparticles/aminated alkaline lignin composite and its catalytic ability[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021,587:334-346. [百度学术]
LÓPEZ D, GIRALDO L J, LUCAS E F, et al. Cardanol/SiO2 Nanocomposites for Inhibition of Formation Damage by Asphaltene Precipitation Deposition in Light Crude Oil Reservoirs. Part I: Novel Nanocomposite Design Based on SiO2-cardanol Interactions[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020,34(6):7048-7057. [百度学术]
OLIVO-ALANIS D, GARCIA-REYES R B, ALVAREZ L H, et al. Mechanism of anaerobic bio-reduction of azo dye assisted with lawsone-immobilized activated carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 347: 423-430. [百度学术]
VAHIDHABANU S, ADEOGUN A I, BABU B R. Biopolymer-grafted, Magnetically Tuned Halloysite Nanotubes as Efficient and Recyclable Spongelike Adsorbents for Anionic Azo Dye Removal[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(1): 2425-2436. [百度学术]
LEI C, PI M, JIANG C, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (ZnO) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of Congo red[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 490: 242-251. [百度学术]
WANG H, LI Z, YAHYAOUI S, et al. Effective adsorption of dyes on an activated carbon prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose: Experiments, characterization and advanced modelling[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128116. [百度学术]
ZHU H, CHEN S, DUAN H, et al. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes using porous chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels: Optimization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123213. [百度学术]
JIN Y, LI Y, DU Q, et al. Porous metal-organic framework-acrylamide-chitosan composite aerogels: Preparation, characterization and adsorption mechanism of azo anionic dyes adsorbed from water[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127155. [百度学术]
ZHAO J, LU Z, HE X, et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Porous Fe(OH)3@Cellulose Hybrid Fibers for Effective Removal of Congo Red from Contaminated Water[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(9): 7723-7732. [百度学术]
WANG X, LIU B, LIU Z, et al. Promising adsorbent for dye detoxification: Exploring the potential of chitosan sodium carboxymethylcellulose silk fibroin aerogel[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129127. [百度学术]
ZHENG Y, ZHU B, CHEN H, et al. Hierarchical flower-like nickel(II) oxide microspheres with high adsorption capacity of Congo red in water[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 504: 688-696. [百度学术]
LI K, YUAN G, DONG L, et al. Boehmite aerogel with ultrahigh adsorption capacity for Congo red removal: Preparation and adsorption mechanism[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122065. CPP [百度学术]